- Developers
- Professional Navigation for Fleets
- Android
- API
- Municipal API for 2D
Municipal API for 2D
Introduction
Municipal navigation is the feature that allows drivers to be navigated in the mode suitable for execution of municipal services. That is, when one needs a navigation in complicated trajectories not always matching the official road network. An example is the waste management service where the vehicle sometimes needs to go off-road or into a forbidden zone and where driver needs to be given custom instructions such as "collect the bin on the right side".
The Municipal feature is supported by use of municipal API functions and OFG json route object, and it is reflected by a special navigation mode called municipal navigation mode, which is triggered by use of LoadOFGRoute API function.
Requirements and limitations
The feature is currently supported only for the 2D navigation version Sygic Fleet 2D release 15i or newer, and under extra licensing
- the navigation license (mlm file) must contain the guided route permission: municipalServices=yes
Integration
Municipal feature is supported with the following API functions.
Note that API functions operate with routes using a proprietary Sygic municipal route format called OFG (municipal offroad guide route format). Therefore we refer to municipal routes as OFG routes.
| SDK Function | Description |
|---|---|
| loadOFGRoute | Loads an OFG route and starts navigation following that route (note: old name was loadGuidedRoute) |
| getOFGRouteStatus | Gets the status of OFG route in JSON format (note: old name was getGuidedRouteStatus) |
| saveOFGRoute | Saves sub-route of currently loaded OFG route (note: old name was saveGuidedRoute) |
| startNavigation | triggers the standard navigation to a starting point of an OFG route |
Usecase example
OFG routes can be imported to navigation from any web based solution, which allows construction and editing of routes. Such tool can apply a simple json conversion and import a route through the Sygic API call loadOFGRoute.
An example of a Municipal route generator shown bellow can be quickly designed using Sygic maps services.
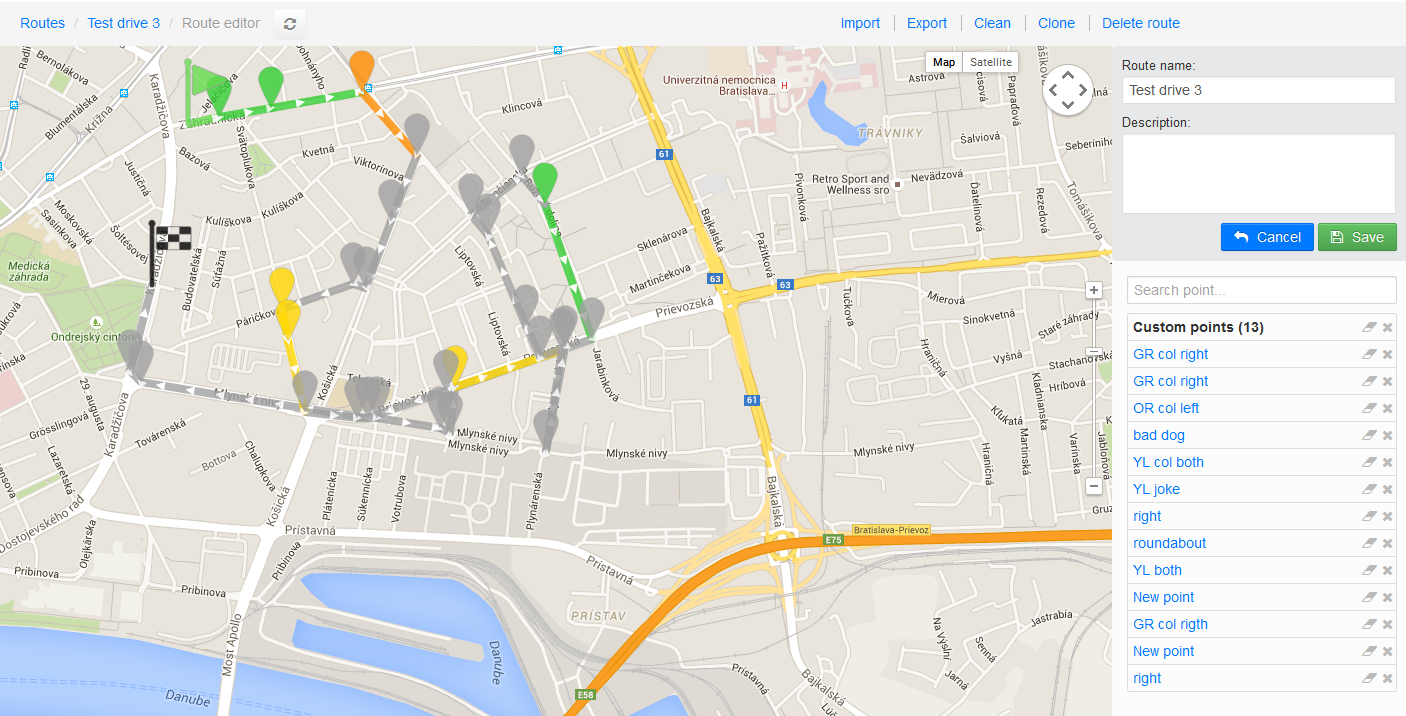
Json Municipal Route object
This route object is used with the SDK function LoadOFGRoute, through which one can send a guided route to the navigation while the navigation switches to the special navigation mode, in which it tries to navigate drivers using the defined geometry, i.e. even on the roads or trajectories not covered by current maps.
Such routes can be extended with additional information such as coloring for visualization and possible TTS messaging.
Route format
The json specification of the supported structure is shown in the diagram bellow. The filenames of this type of route have the suffix ofg.
The fields denoted with * are mandatory.
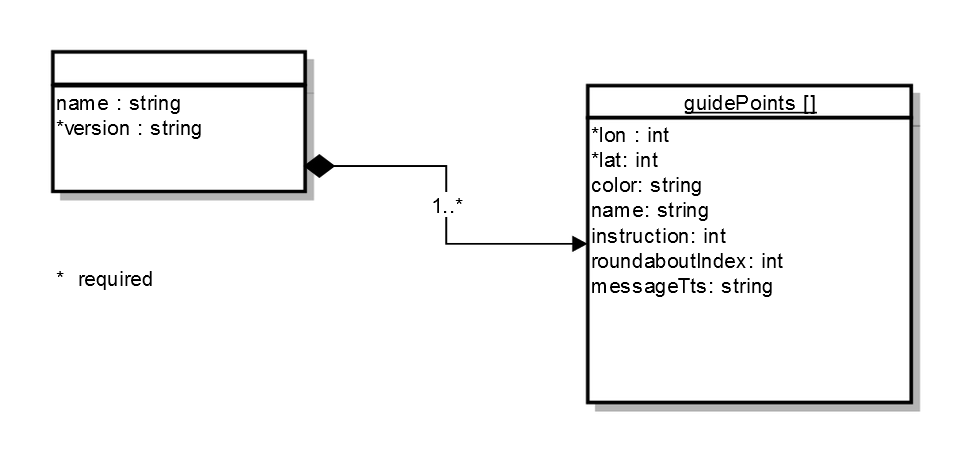
Table of json fields
| Field | Type | Default value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | string | caption on the point | |
| version | string | n/a | the file format version, supported: 1.0.0.2 |
| lat | int | n/a | latitude position defined as WGS84 multiplied by 100,000 |
| lon | int | n/a | longitude position defined as WGS84 multiplied by 100,000 |
| color | string | #C0C0C080 | the color string defined in the format RGBA format, example #FFA0522D. The color is applied on the point and the roadline starting from this point to the next one |
| instruction | int | -1 | defines instruction to be given at the point, -1 denotes the instruction to be inferred automatically, -2 denotes no instruction is given, see the Instruction table bellow for details |
| roundaboutIndex | int | 1 | the exit index defined for roundabout instructions |
| messageTts | string | the text for the spoken instruction at the point |
| Instruction name | int | Index required |
|---|---|---|
| Remove Instruction | -2 | FALSE |
| Inferred Instruction | -1 | FALSE |
| Direction Keep Right | 0 | FALSE |
| Direction Keep Left | 2 | FALSE |
| Direction Easy Right | 4 | FALSE |
| Direction Easy Left | 6 | FALSE |
| Direction Right | 8 | FALSE |
| Direction Left | 10 | FALSE |
| Direction Sharp Right | 12 | FALSE |
| Direction Sharp Left | 14 | FALSE |
| Direction Straight | 16 | FALSE |
| Direction U Turn Right | 17 | FALSE |
| Direction U Turn Left | 18 | FALSE |
| Direction Roundabout SE | 23 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout E | 24 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout NE | 25 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout N | 26 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout NW | 27 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout W | 28 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout SW | 29 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout S | 30 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout SE_LS | 32 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout E_LS | 33 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout NE_LS | 34 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout N_LS | 35 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout NW_LS | 36 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout W_LS | 37 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout SW_LS | 38 | TRUE |
| Direction Roundabout S_LS | 39 | TRUE |
| Direction Ferry | 40 | FALSE |
| Direction State Boundary | 41 | FALSE |
| Direction Exit Right | 43 | FALSE |
| Direction Exit Left | 44 | FALSE |
Version history
| Version | Release date | Change log |
|---|---|---|
| 1.0.0.2 | 28.9.2015 | 1st official release |
| 1.0.0.1 | 29.5.2015 | beta release |
Json example
An example of the route for waste management trip:
{
"name":"Bratislava wastecollection route#1",
"version":"1.0.0.2",
"guidePoints":
[
{
"lon": 1712838,
"lat": 4816011
},
{
"lon": 1712916,
"lat": 4816097,
"color": "#FFA0522D",
"name": "New point",
"instruction": 26,
"roundaboutIndex": 3,
"messageTts": "Collect left"
},
{
"lon": 1712804,
"lat": 4816143,
"color": "#FFB8860B",
"name": "New point",
"instruction": 2,
"messageTts": "Collect both sides"
},
{
"lon": 1712750,
"lat": 4816117
},
{
"lon": 1712630,
"lat": 4816157,
"color": "#FFFFD700",
"name": "New point"
},
{
"lon": 1712650,
"lat": 4816260,
"color": "#FFCD5C5C"
},
{
"lon": 1712968,
"lat": 4816158
},
{
"lon": 1712998,
"lat": 4816195
},
{
"lon": 1712816,
"lat": 4816258
},
{
"lon": 1712712,
"lat": 4816294
},
{
"lon": 1712727,
"lat": 4816356
}
]
}Getting started
In the following we will demonstrate programming of few usecases using API functions for municipal support, which might be helpful for a solution provider.
API functions
| SDK Function | Description |
|---|---|
| loadOFGRoute | Loads an OFG route and starts navigation following that route |
| getOFGRouteStatus | Gets the status of OFG route in JSON format |
| saveOFGRoute | Saves sub-route of currently loaded OFG route |
| startNavigation | triggers the standard navigation to a starting point of an OFG route |
Usecases
| Operation | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Load and unload OFG route | load OFG route and get into municipal navigation mode and back to standard navigation mode |
| 2. Navigate to beginning of OFG route | navigate to beginning of OFG route in order to get ready for OFG navigation mode |
| 3. Pause OFG route | Pause OFG route navigation in order to resume later |
| 4. Resume OFG route | Resume OFG navigation mode at the point it has been previosuly paused |
| 5. Handle off-route scenario | React on off-route events in an appropriate way |
| 6. Join OFG route | Join OFG route in order to handle road obstacles |
| 7. Missed segments | Save missed segments as OFG routes for possibly deferred execution |
1. Load and unload OFG route
In order to load OFG route, call ApiNavigation.loadOFGRoute(pathToOFGFile, 0, FLAG_OFG_DEFAULT, timeout). Navigation will switch to the OFG navigation mode. In this mode vehicle is not snapped to a road network but rather red thin line appears, showing the point on the OFG route closest from your vehicle. If you want to unload OFG route, call ApiNavigation.stopNavigation(timeout). Navigation is then switched back to the standard navigation mode (vehicle snapped to a road network).
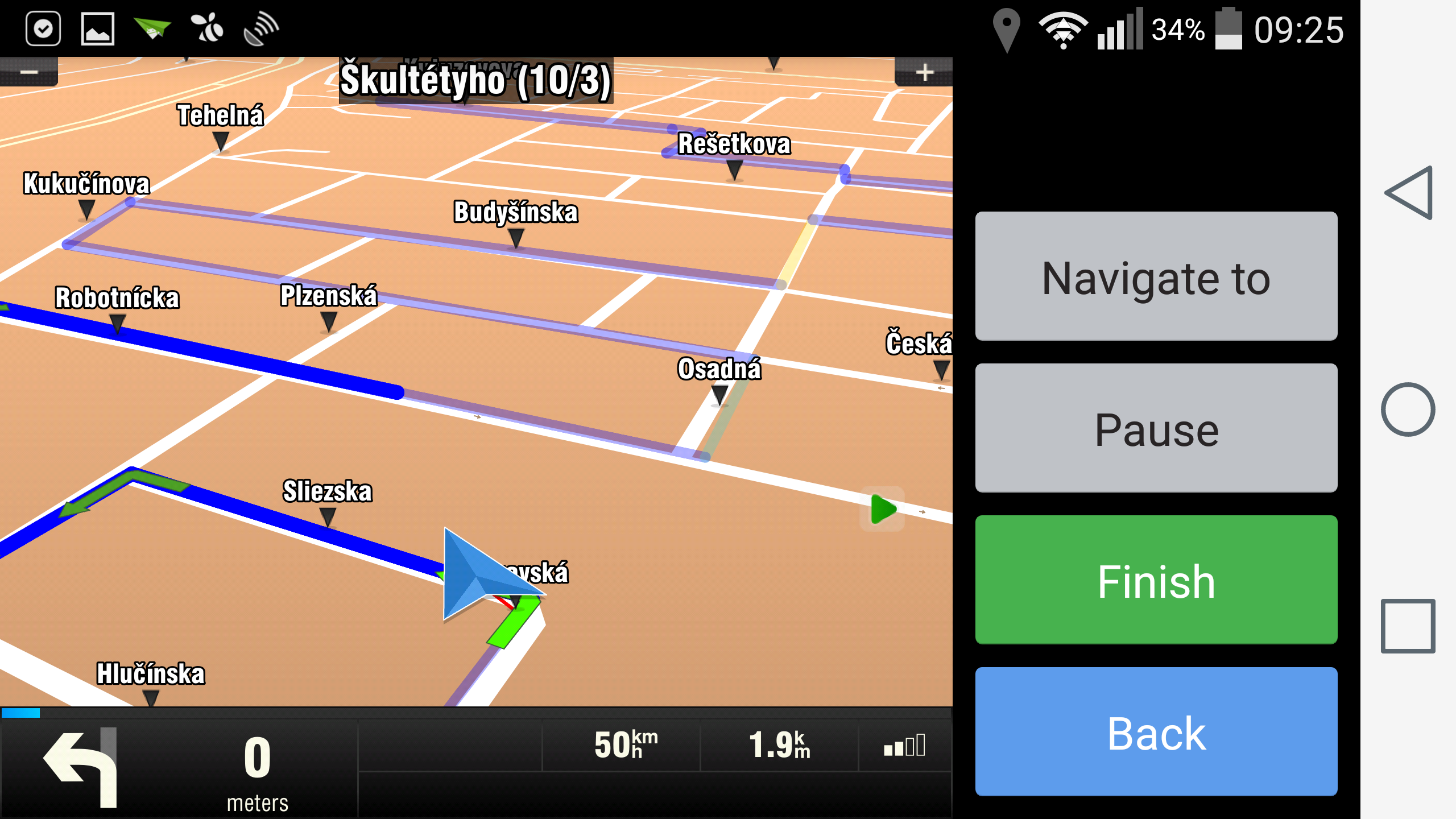
2. Navigate to beginning of OFG route
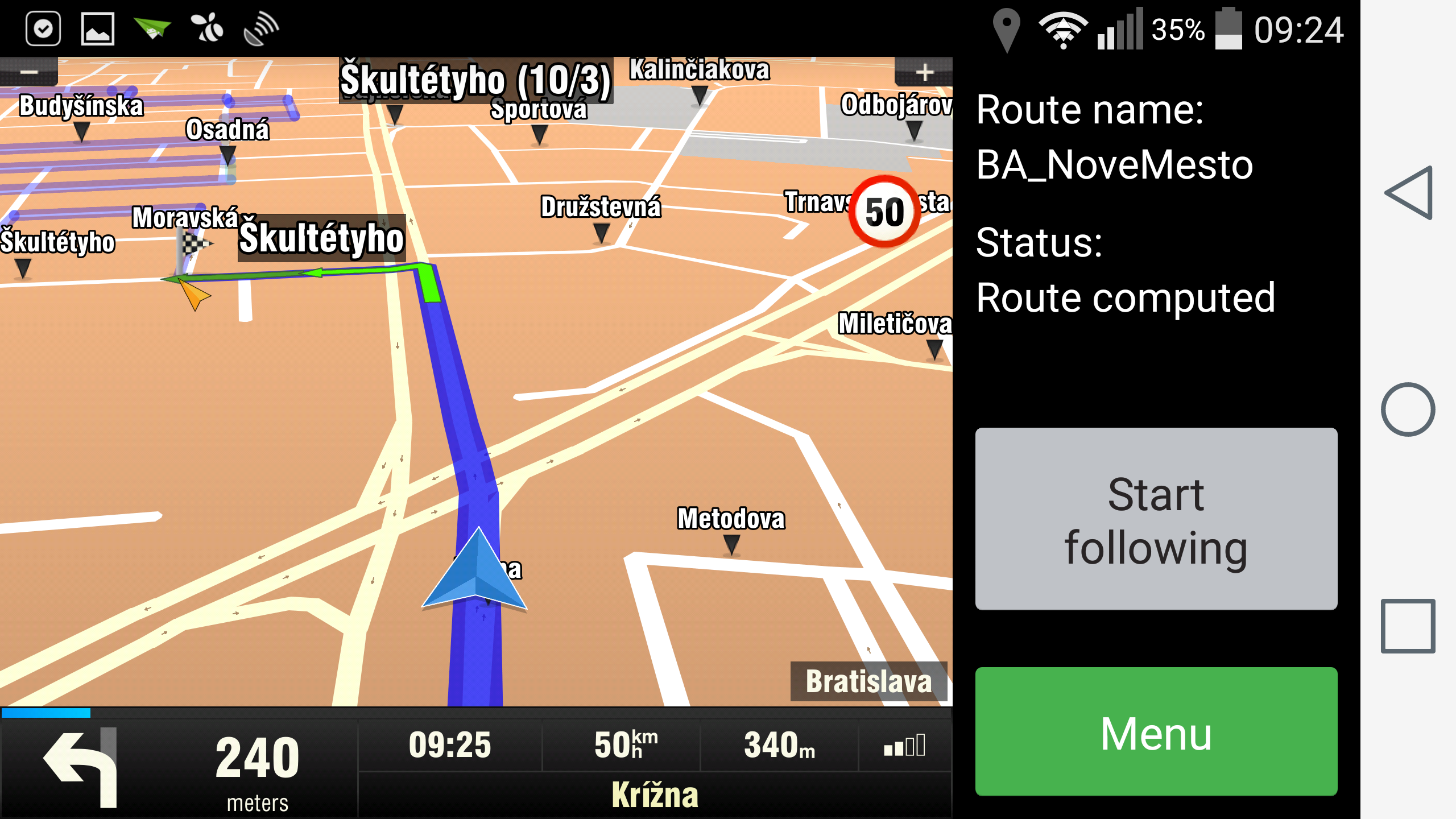
Before loading OFG route, you can consider that driver should be navigated to the beginning of the OFG route using standard navigation mode. First, you will have to discover the start point of the OFG route and the direction of the first OFG segment, so that you are navigated to this point in a correct direction. To get these values, you have to parse the OFG file by yourself or you can use the helper class OfgSegmentInfo (shown in the appendix) to support this functionality. Then you can call ApiNavigation.startNavigation(startOfOFGRoute, 0, false, routeComputeSettings, timeout), where routeComputeSettings is instance of the RouteComputeSettings class and contains the direction angle information. If you want to see the OFG route during navigation to its start, but you don't want to be switched to the OFG navigation mode, call loadOFGRoute with FLAG_OFG_SHOW_ONLY. This will ensure that an OFG route will be visible, but you will stay in standard navigation mode. When arriving to the start point, you will receive EVENT_ROUTE_FINISH. To switch to the OFG navigation just call loadOFGRoute with flag FLAG_OFG_DEFAULT.
Note: You may consider whether to use or not the navigation to the start point of the OFG route. For example if the vehicle is close to the start of an OFG route, you may want to skip navigating to the start point.
OfgSegmentInfo ofgInfo = new OfgSegmentInfo(sRoutePath, 0);
ofgInfo.startWp;
ofgInfo.directionAngle;
try {
if (isCloseToCurrentPosition(ofgInfo.startWp)) {
// start point is close, load OFG route
ApiNavigation.loadOFGRoute(mStrCurrentRoutePath, 0, ApiNavigation.FLAG_OFG_DEFAULT, API_CALL_TIMEOUT);
}
else {
// only show OFG route
ApiNavigation.loadOFGRoute(mStrCurrentRoutePath, 0, ApiNavigation.FLAG_OFG_SHOW_ONLY, API_CALL_TIMEOUT);
// navigate to start point
RouteComputeSettings rcs = new RouteComputeSettings(ofgInfo.directionAngle);
ApiNavigation.startNavigation(ofgInfo.startWp, 0, false, rcs, API_CALL_TIMEOUT);
}
}
catch (GeneralException e) {
...
}
3. Pause OFG route
For some cases you may want to pause the current OFG navigation, get navigated from it in a standard navigation mode and return to the pause point later to continue. First you have to get the current status of the OFG navigation. Use ApiNavigation.getOFGRouteStatus(). From the resulting JSON string you can parse out the current index of OFG route (represents state and the progress of the OFG route execution) and GPS coordinates of vehicle's current position on OFG route. Store these values for the purpose of resuming the route and call ApiNavigation.stopNavigation().
try {
String routeStatus = ApiNavigation.getOFGRouteStatus(API_CALL_TIMEOUT);
// store these values for Resume
mPauseRouteIndex = getRouteIndex(routeStatus);
mPauseRouteWaypoint = getPointOnRoute(routeStatus);
OfgSegmentInfo segInfo = new OfgSegmentInfo(mStrCurrentRoutePath, mPauseRouteIndex);
// store also this value for Resume
mPauseRouteAngle = segInfo.directionAngle;
}
catch (GeneralException e) {
...
}
try {
ApiNavigation.stopNavigation(API_CALL_TIMEOUT);
}
catch (GeneralException e) {
...
}4. Resume OFG route
If you want to return back to the previously paused point, use the same routine as for navigation to start point, but use the values retrieved and stored at Pause route.
try {
if(isCloseToCurrentPosition(mPauseRouteWaypoint))
{
ApiNavigation.loadOFGRoute(mStrCurrentRoutePath, mPauseRouteIndex, 0, API_CALL_TIMEOUT);
}
else
{
RouteComputeSettings rcs = new RouteComputeSettings(mPauseRouteAngle);
ApiNavigation.startNavigation(mPauseRouteWaypoint, 0, false, rcs, API_CALL_TIMEOUT);
}
}
catch(GeneralException e) {
...
}5. Handle off-route situation
If the driver gets too far from an OFG route, EVENT_OFF_ROUTE is triggered. Event data is equal to "1". If the driver comes back in a near proximity to the route, the same event is triggered but with the data equal to "0".
Note that driver will be guided to the point where he left the route. If this point is not reachable, he should be given the possibility to "join" the route (see this usecase in a next section).
public void onEvent(final int event, final String data)
{
if(event == ApiEvents.EVENT_OFF_ROUTE)
{
if(data != null)
{
if(data.compareTo("1") == 0)
// driver got too far from OFG route
else
// driver is back on OFG route
}
}
}
6. Join OFG route
If the user is off route and he cannot reach his abandoned position on the OFG route, he should be able to continue following the route from his current position. In this case call loadOFGRoute with startIndex -1. This will reset driver's current position on the OFG route to the closest point on route to vehicle.
ApiNavigation.loadOFGRoute(pathToOFGFile, -1, FLAG_OFG_DEFAULT, API_CALL_TIMEOUT)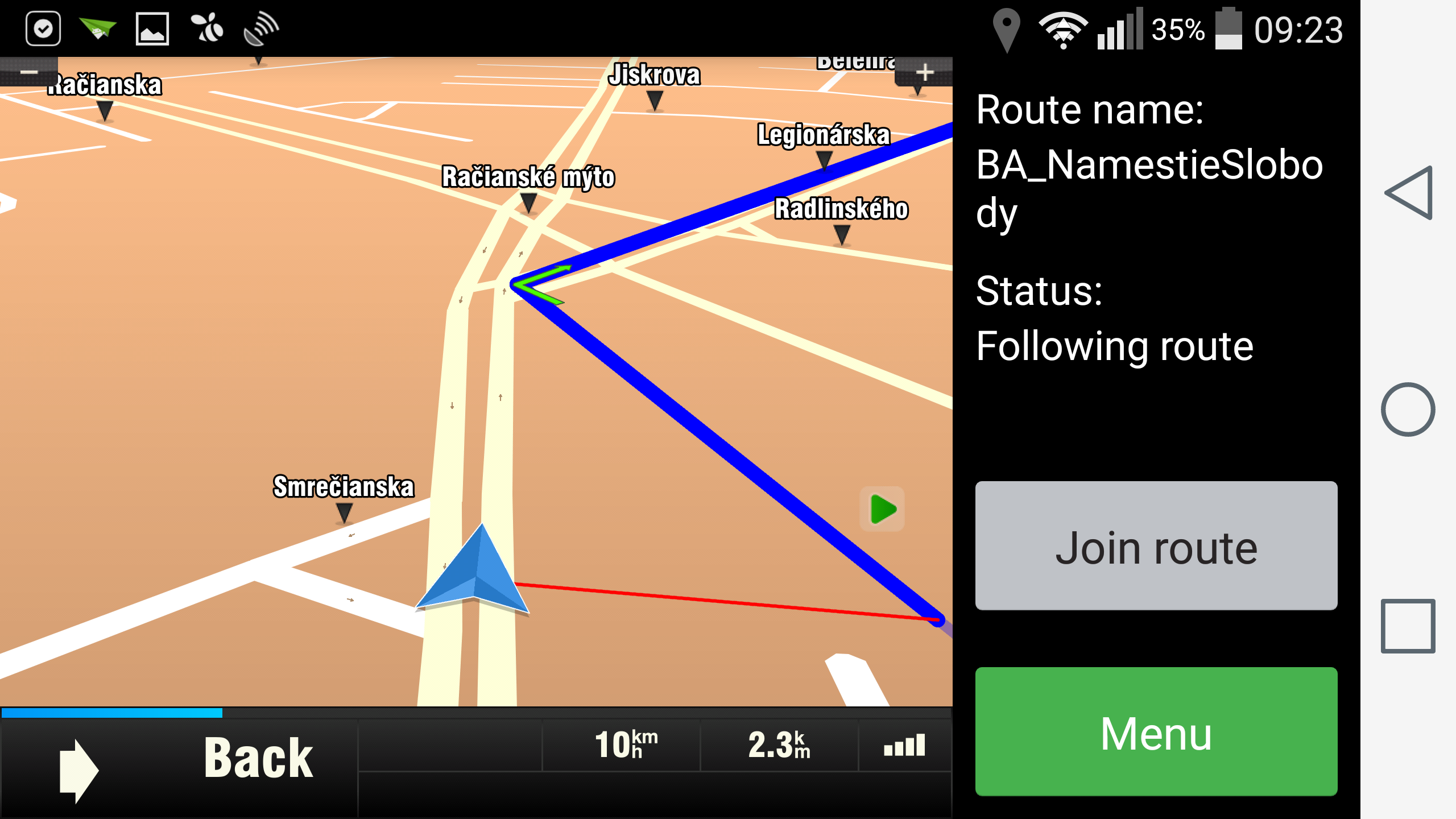
7. Missed segments
If the driver avoids a part of the route (e.g. due to it was not reachable), you may want to store this part of the route as a missed segment for future handling. Use saveOFGRoute(fileName, fromIndex, fromPos, toIndex, toPos, timeout) to save a particular subroute of the currently loaded OFG route. There are 3 scenarios for this case:
1. Driver could not reach the start point (Start following)
Driver should be able to join the route. After joining the route, get the current OFG route status. This will give you his current position and route index. Use these values as parameters (toPos and toIndex) for saveOFGRoute. Setting start point to null and start index to -1 will ensure that the saved subroute will have the start in the same point as the original route.
ApiNavigation.saveOFGRoute(fileName, -1, null, toIndex, toPos, API_CALL_TIMEOUT)2. Driver could not reach the end of the route
Driver should be able to end the route prematurely (e.g. due to the end point is not reachable). Before unloading the route, get the route status to get actual point and index. Use these values as parameters (fromPos and fromIndex) for saveOFGRoute. Setting end point to null and end index to -1 will ensure that the saved subroute will the end in the same point as the original route.
ApiNavigation.saveOFGRoute(fileName, fromIndex, fromPos, -1, null, API_CALL_TIMEOUT)3. Driver had to avoid an inner part of the route
In this situation you have to work with Off route event. If the driver gets too far from a route, get the route status to get current point and current index on the OFG route (start of missed segment) and store it. After joining the route, do the same to get the end point and end index of missed segment.
ApiNavigation.saveOFGRoute(fileName, fromIndex, fromPos, toIndex, toPos, API_CALL_TIMEOUT) Note: You can set the minimal length of the missed segment in the application's settings.ini file (m_nGuidedMinSaveRouteLength). If you try to save a shorter subroute, function will fail and will give you a notification about this.
Appendix: OfgSegmentInfo helper class
package com.sygic.routeloader;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import com.sygic.sdk.api.model.Position;
import com.sygic.sdk.api.model.WayPoint;
public class OfgSegmentInfo {
public WayPoint startWp = null;
public int directionAngle = -1;
public OfgSegmentInfo(String filePath, int segment) {
parse(filePath, segment);
}
private void parse(String filePath, int segment) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
File file = new File(filePath);
FileReader reader;
try {
reader = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
String line;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(line);
}
reader.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
return;
}
try {
JSONObject jRoute = new JSONObject(sb.toString());
JSONArray jPoints = jRoute.getJSONArray("guidePoints");
if(jPoints.length() > segment) {
JSONObject jPoint = jPoints.getJSONObject(segment);
int lon = jPoint.getInt("lon");
int lat = jPoint.getInt("lat");
startWp = new WayPoint("Start", lon, lat);
}
if(jPoints.length() > segment + 1) {
JSONObject jPoint = jPoints.getJSONObject(segment + 1);
int lon = jPoint.getInt("lon");
int lat = jPoint.getInt("lat");
Position startPos = startWp.getLocation();
directionAngle = getDirectionAngle(startPos.getX(), startPos.getY(), lon, lat);
}
} catch (JSONException e) {
return;
}
}
private int getDirectionAngle(int fromX, int fromY, int toX, int toY) {
double dFromX = (double)fromX;
double dToX = (double)toX;
double dFromY = (double)fromY;
double dToY = (double)toY;
double dWorkX = dToX - dFromX;
double dWorkY = dToY - dFromY;
double dAngle = Math.atan(dWorkY / dWorkX);
dAngle *= 57.29578; // to degrees
if(dWorkX < 0)
dAngle += 180.0;
int nAngle = 90 - (int)dAngle;
// normalize angle:
nAngle %= 360;
if(nAngle < 0)
nAngle += 360;
return nAngle;
}
}- Previous article: Municipal API
- Next article: Custom URL


